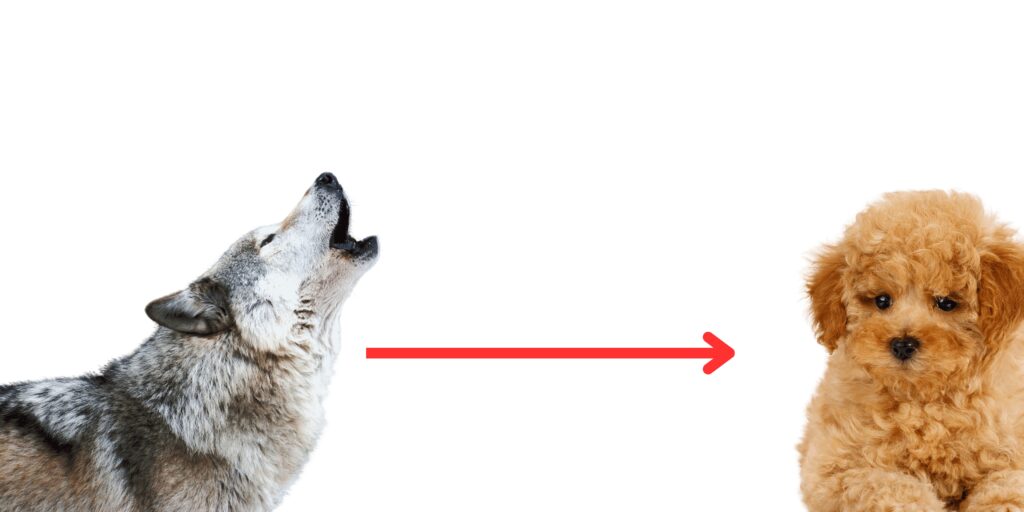
Dogs have been our loyal companions for millennia, but their journey from wild wolves to the diverse breeds we know today is a testament to their remarkable evolution. In this article, we’ll explore the fascinating history and genetic adaptations that have shaped the evolution of dogs, from their ancestral origins to their roles in modern society.
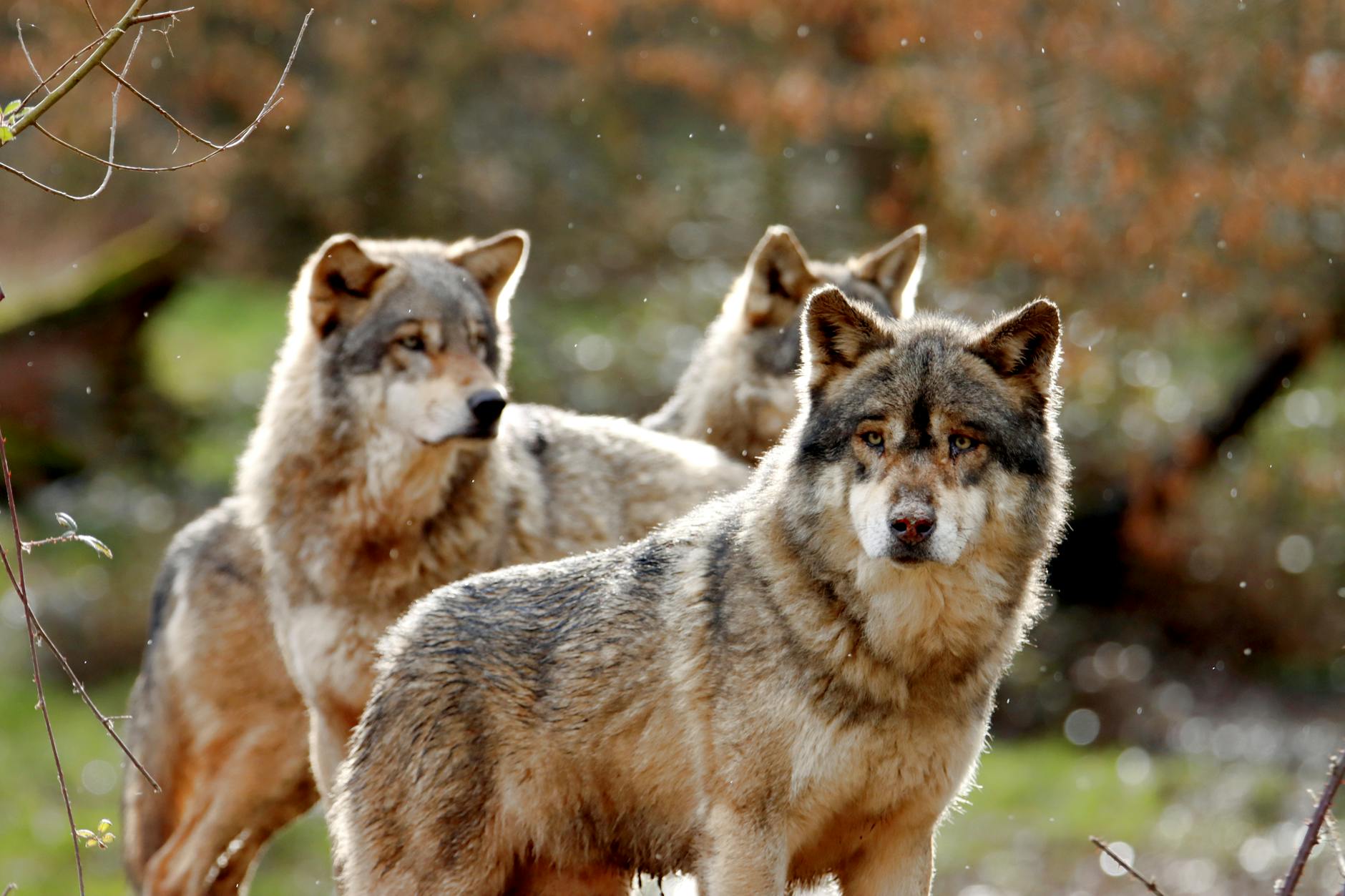

Domestication of Wolves
The domestication of dogs from wolves is a topic of ongoing study and debate among scientists. Evidence suggests that early humans began domesticating wolves tens of thousands of years ago, possibly attracted to their hunting prowess and protective instincts. Over time, selective breeding led to changes in behavior and appearance, laying the foundation for the diverse breeds we see today.
Diversity of Dog Breeds
From the majestic Siberian Husky to the elegant Poodle, dogs come in a staggering variety of shapes, sizes, and temperaments. The development of different breeds can be traced back to specific historical periods and geographical regions, where dogs were selectively bred for specific tasks such as hunting, herding, guarding, and companionship.
Genetic Adaptations
Genetic studies have revealed significant differences between wolves and modern dogs, including changes in genes related to digestion, metabolism, and behavior. Domestication has also led to physical adaptations, such as smaller jaws and teeth, which reflect dogs’ shift from a carnivorous diet to one more suited to human-provided food.
Evolutionary Timeline
The timeline of dog evolution is marked by key archaeological discoveries and genetic analyses. For example, the transition from ancient wolf populations to early dog breeds can be seen in fossil remains and DNA evidence from ancient dog burials. These findings provide insights into the early stages of human-dog coexistence.
Selective Breeding and Modern Breeds
Selective breeding practices accelerated during the Victorian era, resulting in the creation of distinct dog breeds with specific traits and appearances. Breeding clubs and standards formalized the characteristics of breeds, shaping them into the companion animals and working dogs we recognize today.
Behavioral Evolution
Behavioral changes from wolves to dogs include reduced aggression, increased socialization with humans, and the ability to interpret human gestures and emotions. These adaptations have strengthened the bond between humans and dogs, making them indispensable partners in various roles, from service animals to beloved pets.
Human-Dog Relationship
Throughout history, dogs have served as hunters, protectors, herders, and companions, forging a unique partnership with humans that has influenced both species’ evolution. Dogs’ ability to understand human communication and emotions has enhanced their utility and endearment in households and societies worldwide.

Impact of Modern Lifestyle
In recent centuries, urbanization and shifts in human lifestyles have further shaped the evolution of dogs. Changes in diet, living environments, and breeding practices have impacted their health, behavior, and genetic diversity. Understanding these influences is crucial for ensuring the well-being and sustainability of dog populations in contemporary society
The evolution of dogs from wolves to the diverse array of breeds we cherish today is a testament to their remarkable adaptability and the enduring bond between humans and animals. By exploring their evolutionary journey, we gain a deeper appreciation for their role in shaping our shared history and enhancing our lives.
